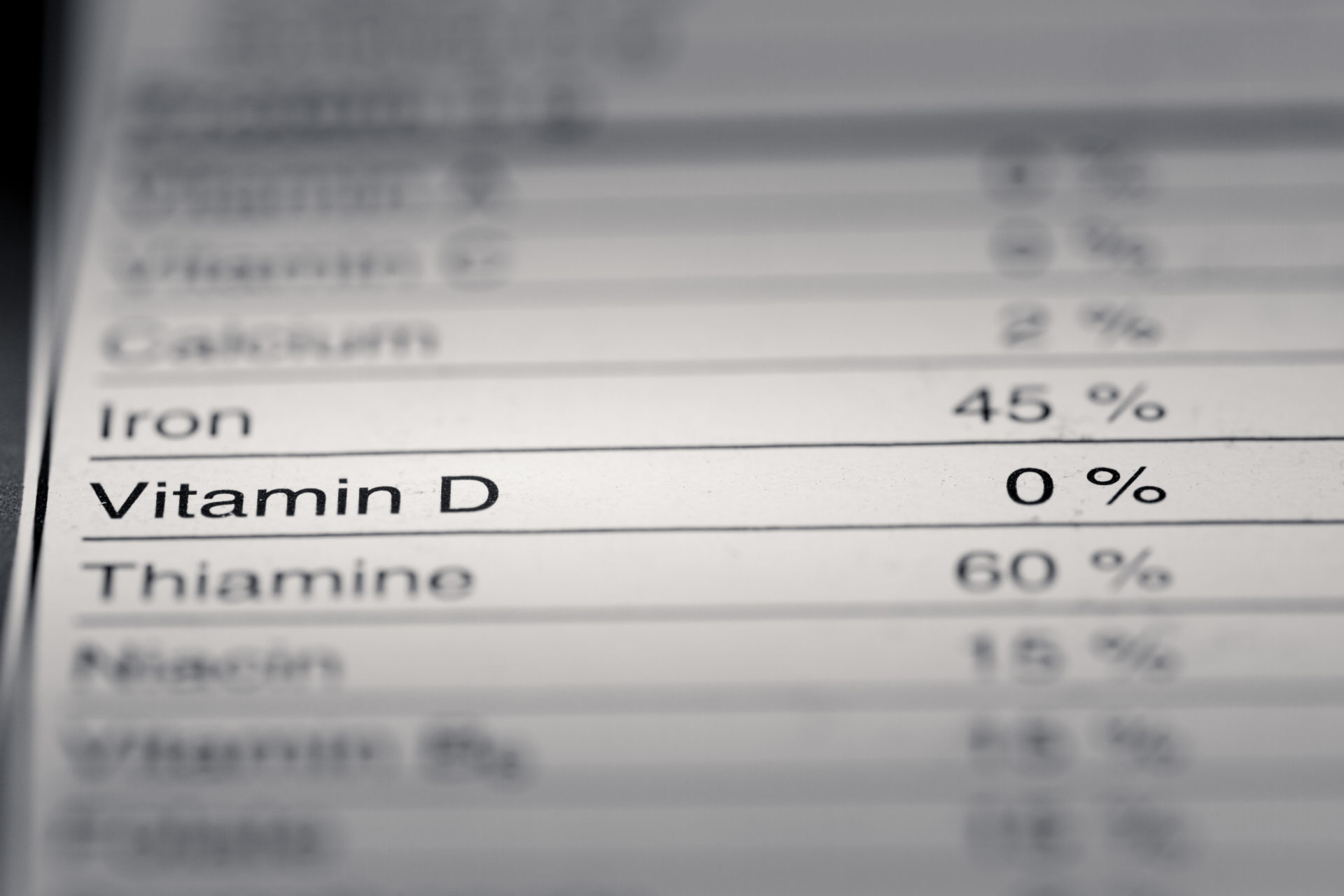
The importance of Vitamin D
No vitamin D through windows
I am sitting in front of a large window, enjoying the warmth that is coming through the glass onto my back. It’s lovely. And quite a change from the wintry weather that has only just passed. How disappointing that this doesn’t translate to vitamin D benefits.
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin that has a key role in helping calcium be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract to support the growth and maintenance of our bones, as well as controlling calcium levels in the blood.
Studies show that Australian women do not get enough vitamin D. This is linked to several health issues, including fatigue, low mood, joint and muscle pain, muscle weakness and bone density problems.
After realising that we can’t get vitamin D through a summery window, I did some research to find out how to actually increase our vitamin D levels. There seems to be limited options.
1. Vitamin D3 Supplements
2. Foods
Vitamin D can be obtained from some foods such as fatty fish, liver, eggs, margarine and some milk products. But the Vitamin D Council states
Most foods that contain vitamin D only have small amounts, so it’s almost impossible to get what your body needs just from food.
3. Sunlight
The body is designed to produce vitamin D3 when bare skin is exposed to the ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from sunlight. This is the most natural way to get vitamin D and works best by exposing a large area of skin, such as the back, rather than small areas like face or arms.
The amount of vitamin D benefit from exposing bare skin depends on factors including:
- Skin colour – paler skin make vitamin D more quickly than darker skins because of melanin protection.
- Amount of skin exposed – the more skin your expose the more vitamin D your body will produce.
- Age – skin has a harder time producing vitamin D as we age.
- Sunscreen – this blocks a lot of vitamin D production.
- Clouds – less UVB reaches your skin on a cloudy day so your skin makes less vitamin D.
- Air pollution – polluted air soaks up UVB .
- Windows – glass blocks all UVB. No vitamin D is produced in sunlight behind glass.
According to the Cancer Council of Australia, we need to balance the risk of skin cancer caused by too much sun exposure, with maintaining adequate vitamin D levels. Their website provides the following facts:
- Sensible sun protection does not result in vitamin D deficiency.
- For most people, adequate vitamin D levels can be reached through incidental exposure to the sun. During summer, most people can maintain adequate vitamin D levels from a few minutes of exposure to sunlight on their face, arms and hands on most days of the week.
- In winter, we may need about two to three hours of sunlight to the face, arms and hands, spread over a week.
Further reading